Physiotherapy For Pleural Effusion
The area between the layers of tissue that line the lungs and the chest cavity, known as the pleural space, can get filled with either transudate or exudate forms of fluid. Transudate is usually composed of ultra-filtrates of plasma due to an imbalance in vascular hydrostatic and oncotic forces in the chest, while exudate is typically produced by inflammatory conditions. Exudative pleural effusions are usually more serious and difficult to treat. Most pleural effusions are not serious by themselves, but some require treatment to avoid problems. Let’s take a look at how physical therapy helps.
What causes pleural effusions?
There are various factors that can cause fluid to build up in the pleural region. The following is a list of some of the major causes:
- Congestive heart failure
- Kidney failure
- Infection
- Malignancy
- Pulmonary embolism
- Hypoalbuminemia
- Cirrhosis
- Trauma
What are the symptoms?
A minor pleural effusion may not cause any symptoms. Symptoms are more likely when a pleural effusion is moderate or large-sized, or if inflammation is present. Symptoms of pleural effusions may include:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain, especially on breathing in deeply
- Fever
- Cough
How are pleural effusions diagnosed?
A doctor may suspect a pleural effusion based on a person’s symptoms and physical examination. Most often, pleural effusions are discovered on imaging tests. Common tests used to identify pleural effusions include:
- Computed tomography: Compared to chest X-rays, CT scans produce more detailed information about pleural effusions and other lung abnormalities.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound can help guide drainage and identify whether pleural effusions are free-flowing.
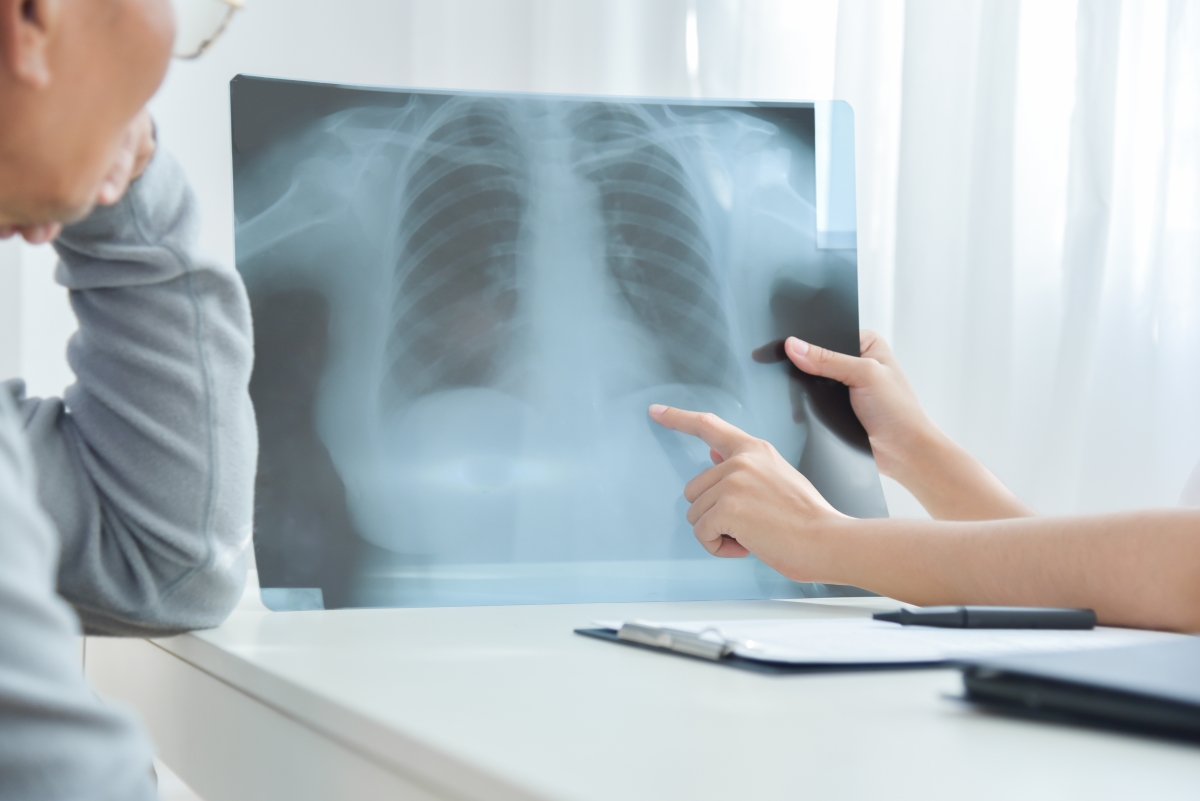
- Chest X-ray film: X-ray films of the chest are often the first step in identifying a pleural effusion. Pleural effusions appear on chest X-rays as white space at the base of the lung.
How are pleural effusions treated?
In mild cases of pleural effusions, your physician may target the underlying medical condition that is causing pleural effusion. For example, prescribing antibiotics for pneumonia or diuretics for congestive heart failures. Large, infected, or inflamed pleural effusions often require drainage to improve symptoms and prevent complications. Various procedures may be used to treat pleural effusions, including:
- Thoracentesis
- Tube thoracotomy
- Pleurodesis
- Pleural drain
- Pleural decortication
How does physiotherapy help?
Physiotherapy is primarily concerned with developing, maintaining, and restoring an individual’s maximum movement and functional ability. For patients with respiratory conditions, physiotherapy includes, but is not limited to, chest physiotherapy or clearance of secretions, and breathing exercises. Respiratory physiotherapy is recommended and should be applied during the first weeks of treatment.
Your lungs play an important role in maintaining and stabilizing oxygen and CO2 levels in your body. Healthy lungs mean you will be able to live a much better quality of life. Don’t live with the fluid congestion of pleural effusions. Consult with our team of expert physical therapists today.







